Chiral plasmonic nanostructures have huge potentials in applications negative refractive index materials, sub-wavelength optical imaging, optical cloaking and ultrasensitive sensing. Over the past years, bottom-up self assembly has been extensively used in building well-defined chiral plasmonic nanostructures, including gold nanoparticle tetramers, spheroidal gold nanoparticle dimers, gold nanoparticle single helix and double helix, etc. However, controlled assembly of anisotropic plasmonic nanomaterials into precisely-defined chiral superstructures, remains an extreme challenge.
Prof. Wang Qiangbin’s group from Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech & Nano-Bionics, CAS, has recently successfully assembled spatially-controlled AuNR chiral superstructures using DNA origami template. The spatial parameters including inter-rod distance and inter-rod angle were precisely defined. They also realized the customized chiral optical properties by designing the three-dimensional configurations of the assembled chiral AuNR superstructures. In their study, bifacial DNA origami is used as template, in which DNA capturing stands are arranged into a straight line on each side of the origami and form a centrosymmetric ‘X’ pattern, so that AuNRs modified with the complementary DNA sequences were bound onto the 2D DNA origami, stacked along the normal direction and rotated around the normal direction. By designing the inter-angle of ‘X’ pattern of the DNA capturing strands, for example, 45° and -45°, they obtained right-handed and left-handed AuNR superstructures, respectively.This work has been published in J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 457–462.
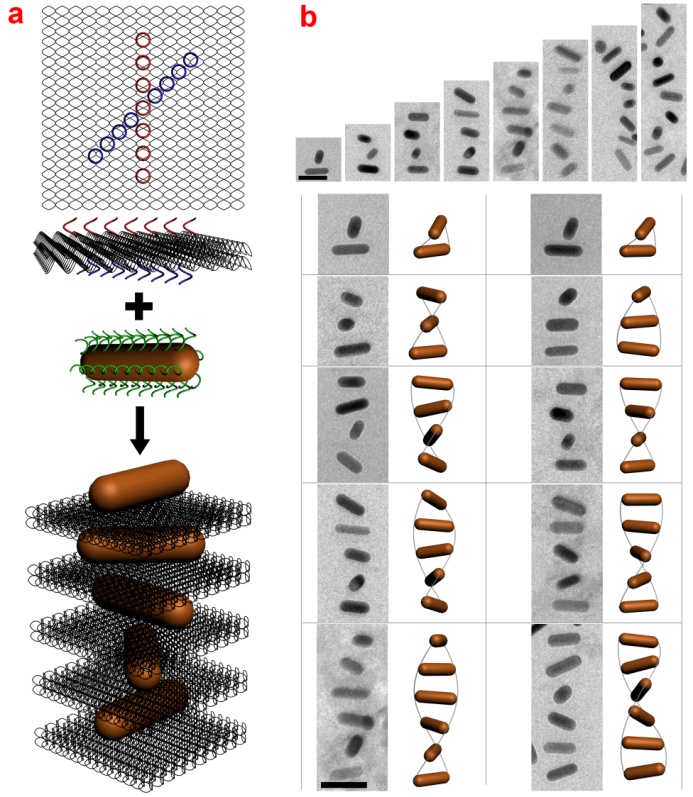
figure1. scheme of the assembly of right-handed AuNR helix and Cryo-EM of AuNR helices with varying length.(Image by SINANO)
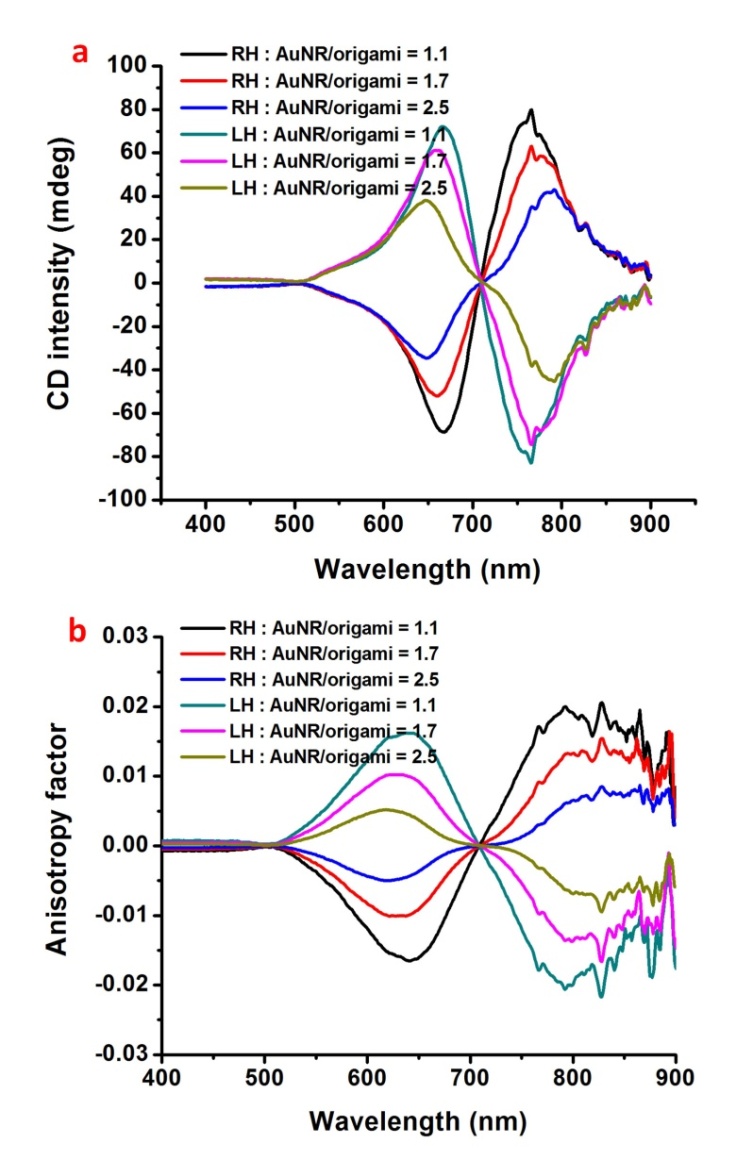
figure2. Circular dichroism and anisotropic factors of AuNR helices with varying average length, which result from different AuNR/origami molar ratio.(Image by SINANO)
downloadFile
