microRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small single-stranded noncoding RNAs, about 22 nucleotides long that have been found in animals, plants, viruses and other species. miRNAs have important roles in plant and animal development, apoptosis, growth control and hematopoietic differentiation. Owing to the impressive progress in understanding the correlations between miRNA expression and diseases, miRNAs have been considered novel biomarkers of various human diseases including, cancer, viral diseases, cardiovascular disorders, metabolic disturbances, etc.
Recently, Prof. LI Jiong’s group from Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech & Nano-Bionics (SINANO), in collaboration with Prof. YAN Xiyun’s group of Institute of Biophysics, CAS, has designed a hybridization-triggered fluorescence strategy for label-free high-throughput miRNA expression profiling, which is superior to most existing chemical and enzymatic labeling methods in the following aspects: (i) fluorescent signaling without the aid of enzymes; (ii) sharp specificity toward end sequence variations and mature/precursor miRNAs; (iii) excellent sensitivity with a linear dynamic range over four orders of magnitude; and (iv) substantial reduction of expenses on reagents, labor and time. This work has been recently published in Nucleic Acid Research (Click here to view paper).
This work was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
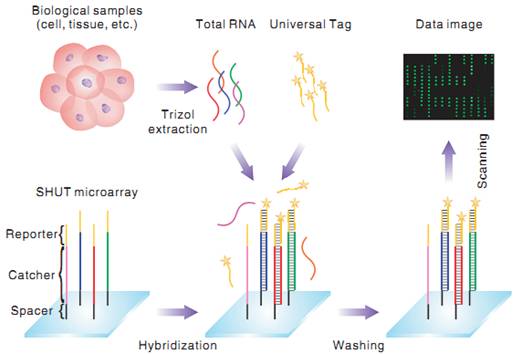 |
|
Figure 1: A schematic diagram of the Stacking-Hybridized Universal Tag (SHUT) assay
Image by SINANO |
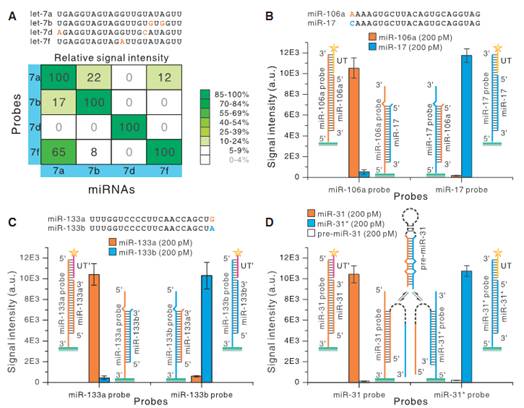 |
|
Figure 2: Specificity of the SHUT assay
Image by SINANO |

