Near-Infrared Quantum Dots (NIR-QDs), especially for the QDs with emission in the second near-infrared window (1000 nm-1400 nm), have advantage of higher penetration depth and signal-to-noise ratio for in vivo imaging, due to its minimal autofluoresence and negligible tissue scattering and absorbance.
Qiangbin Wang’s research group in Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech & Nano-Bionics, CAS, firstly reported a new type of NIR-II Ag2S QDs (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1470-1471). After that, in collaboration with Prof. Hongjie Dai in Stanford University. they executed the cellular imaging by using Ag2S QDs and systematically studied the cytotoxicity of Ag2S QDs. The results showed that the bioconjugation of Ag2S QDs with specific ligands achieved targeted labeling and imaging of different cell lines, and Ag2S QDs had negligible cytotoxicity (ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3695-3702). Furthermore, they clearly imaged the tumor in tumor-bearing Balb/c mice in vivo by injecting the Ag2S QDs via the tail vein (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9818-9821).
Based on the above work, they carefully studied the Ag2S QDs toxicity in vivo, including the long-term in vivo biodistribution of Ag2S QDs and pharmacokinetics and potential effect of Ag2S QDs on the body weight, blood and organs. The results indicated that Ag2S QDs are mainly accumulated in the reticuloendothelial system (RES), such as liver and spleen, after intravenous administration, and can be gradually cleared mainly through the biliary pathway in mice. Ag2S QDs do not cause appreciable toxicity at the concentration of 30 mg/kg (triple of imaging concentration). This work has been recently published in Biomaterials (2013, 34, 3639-3646).
This work was support by funding from CAS “Hundred Talents” program and “Strategic Priority Research Program”, NSFC, NSF Jiangsu Province and MOST.
International Edition.
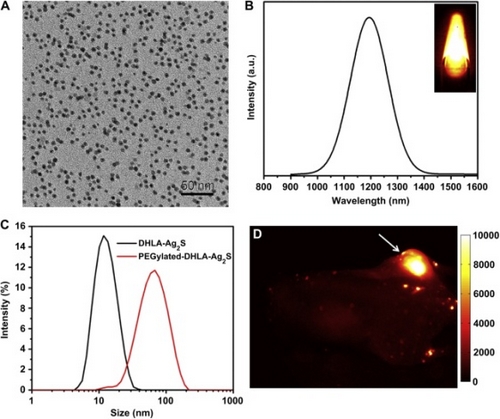
Figure 1. (A) TEM image of the Ag2S QDs ; (B) An NIR- II PL emission spectrum of the Ag2S QDs; (C) The hydrodynamic size distributions of Ag2S QDs with two different surface; (D) An NIR- II PLimage collected in the 1100-1700 nm region of a tumor-bearing Balb/c mouse treat with a 10 mg/kg dose of Ag2S QDs at 24 h p.i.
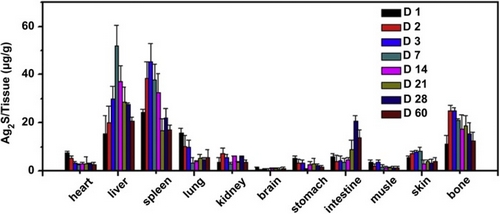
Figure 2. Long-term biodistribution of Ag2S QDs in mice.

