Ionic polymer-metal composite (IPMC) material is a kind of electrochemical actuator with sandwich like structure in which a semi-permeable ion-exchange polymer membrane was covered with two electrode layers. Due to its low actuation voltage, large displacement and good controllability, they are good candidates for light-weight bionic systems, and thus is of important scientific significance and application value. Since its actuation mechanism is mainly ascribed to the ion migration under electric field, key problems including strain relaxation, low strain and strain rate still existed, which were caused by the intrinsic properties of noble metal electrodes and hydrated ions.
In order to improve their ionic actuation performance and stability, Wei Chen’s group focused their research on intelligent multi-scale composite electrode materials in recent years. The main development was about the new type of electrochemical actuators based on three dimensional porous flexible carbon nanotube/grapheme electrodes and ionic liquid based interlayer electrolyte. According to them, the electrode surface enhanced energy storage and electric mechanical coupling mechanisms in non-water and non-metal electrochemical actuation systems were revealed. Moreover, the rapid ion migration and high electrostrictive performance under low voltage were realized. Thus, advanced composite materials with high-frequency electromechanical response, high stability and larger deformation capability were obtained. Based on the above results, a series of research results were published on international scientific magazine and journals (Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 3745;Adv. Mater.,2012, 24, 4317;Adv. Mater.2013, 25, 1270;ACS NANO, 2010,4,1042;ACS NANO, 2010, 4, 3498;Chem. Comm., 2012, 48, 3978) during 2012-2013 and attracted the wide attention of domestic and foreign counter parts.
Recently, by combining the domestic and international development condition of ionic flexible electrochemical actuators, Chen’s group made a detailed and comprehensive analysis on the compositional and structural effects of carbon (especially carbon nanotube and graphene) based electrode materials on their actuation performance and proposed prospect for their future development, which was recently published on 《Advanced Materials》as s review article (Adv. Mater.,2014,26,1025).
The work is supported by the National Natural ScienceFund project, the Ministry of science and technology of major scientific research projects and Jiangsu Province Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars.
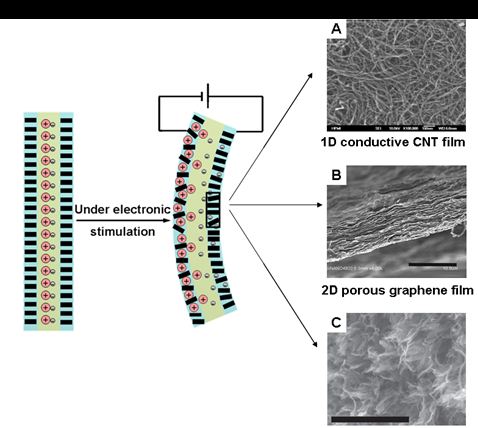
Figure 1.Schematic illustration of actuation mechanism for ionic electrochemical actuators and the development of carbon based electrode materials.(Image By SINANO)

