The ever-growing energy-storage demands, driven by the needs of portable electronic devices, electrical vehicles, and smart grid integration of intermittent renewable electricity sources, have generated a great deal of interests in exploring energy-storage systems with higher capacity, better safety and lower cost than today’s lithium–ion batteries. Among these high energy density battery systems, solid-state lithium batteries are considered highly promising due to their high energy density and good safety because of the absence of flammable organic liquid electrolytes. However, several technical bottlenecks are still holding solid state battery technology back from massive practical applications, one of which is the interfacial problem. The transportation of Li+ ions across the interfaces between solid-state electrolyte and electrodes is currently believed to limit the performance of the solid-state batteries.
Recently, Prof. CHEN Liwei(Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics) and Prof. PENG Zhangquan(Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry) from Chinese Academy of Sciences have published a perspective article entitled “Unlocking the Energy Capabilities of Lithium Metal Electrode with Solid-State Electrolytes” in Joule, a new energy journal launched last fall by Cell press, to discuss the interfacial challenges in solid-state batteries.
In this perspective, they focus on the lithium electrode | solid state electrolyte interface, outline the reaction and process occurring during the stripping/plating of the lithium at the interface, identify the challenges and the interplay between the challenging factors that need to be addressed for a high performance lithium electrode, exemplify the advanced research techniques that can be used to interrogate the interface buried between solid phases, and finally propose approaches towards solving the interface challenge.
This Perspective on the interfacial challenges of solid state lithium batteries is believed to be beneficial for both beginners and veterans in this rapidly evolving field.
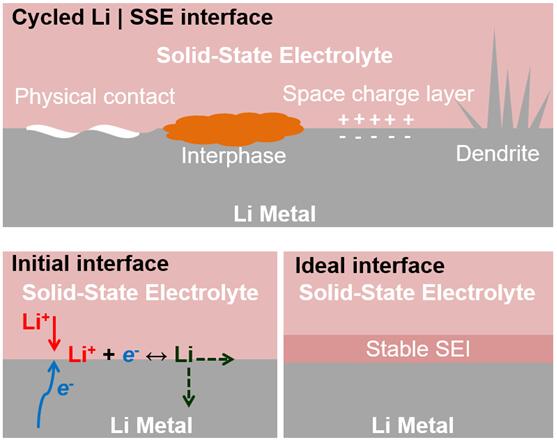
The lithium | solid state electrolyte interface is a major bottleneck limiting the performance of solid state lithium batteries. A number of interrelated factors such as physical contact, parasitic reaction, space charge layer, and dendrite growth affect the impedance and the stability of the interface. Functional interlayers, artificial SEI and hybrid electrolyte may help to address the challenges and improve solid state batteries.(Image by SINANO)
Contact information:
Prof. CHEN liwei, Suzhou institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionic, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Email:lwchen2008@sinano.ac.cn

